Overfilled e-chains and their consequences
Jen Chen | May 13, 2022
I stuff another shirt into my luggage or another piece of wood into the already packed fireplace. “There’s still some space there!” This is also often the motto in everyday life. I often see the same picture with regard to cables in energy chains. Therefore, in this post I would like to educate about overfilled e-chains.

Overfilled energy chains
I have lost count of how many cluttered energy chains I have seen when visiting customers in different countries.
Energy chains also have a maximum capacity. For reliable operation of the system, this should not be exceeded. Otherwise, this can have negative effects of a mechanical but also electrical nature.

Mechanical consequences of overfilled energy chains
e-chains have maximum fill weights. These are determined based on speed, acceleration, vibration, particles and temperature.
If you increase one of these factors above the recommended limit, this can not only pose safety risks but also have a negative impact on the service life.
Overfilling can cause separators or parts of the interior separation to shift, bend or even break. In addition, cables lie directly on top of each other in a crowded e-chain. Due to the friction of the outer jackets, the wear is significantly greater. In addition, great friction can occur between the outer jacket of the cable and the plastic of the energy chain. This also increases the risk of a defective cable.
Too many cables in one chamber or the use of too many cables without a clean interior separation often also leads to the so-called corkscrew effect.

Electrical consequences of overfilled energy chains
As a result, cables can cause jacket or core breaks. This often leads to short circuits or, for example, loss of data on bus cables.

Clearance space in energy chains
The following drawings show the required space reserves in energy chains. In addition to other criteria, the professional filling of the chains is also important for the guaranteed service life of our cables.
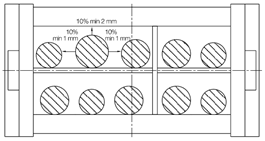
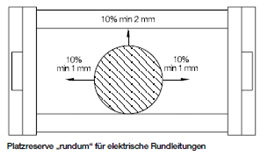
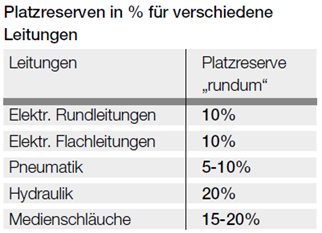
We recommend using clearance space of different sizes depending on the type of cable. In the following table you can read the recommended % values.
Overfilled e-chains often begin as a result of defective cables not being replaced, but simply being supplemented by another cable.
Another form of overload is that machines are updated over time. New functions are added and so the number of cables in the energy chain increases.
Your application – together with igus
We offer numerous online tools to help you choose the right cable. In addition to a service life calculator, there is the new product finder.
In many cases, however, a personal discussion or a visit by a specialist on site can also help. In case you would like to have your chains checked for overfilling or need advice for a new application … We are here for you!
